Cell
The Cell
Cell Cycle and Division
Nucleus
Ribosomes
Mitochondria
Chloroplasts
Proteins
Enzymes
The Human Body
Human Body
Brain
Nervous System
Digestive System
Sight and the Eye
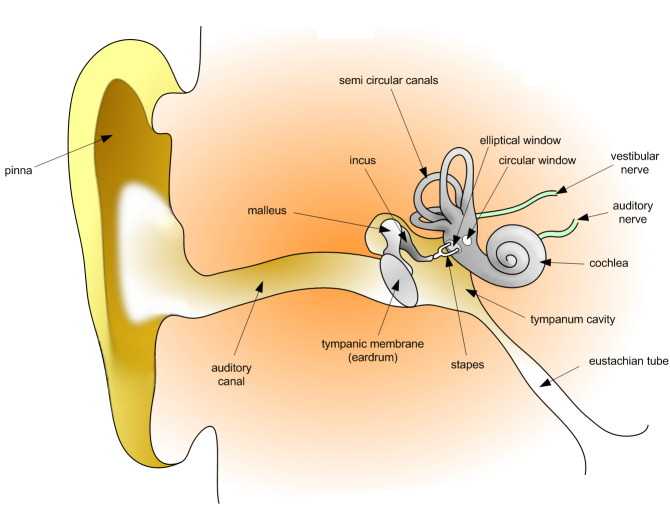
Hearing and the Ear
Smelling and Tasting
Skin
Muscles
Breathing
Blood and Heart
Bones
List of Human Bones
Immune System
Organs
|
Nutrition
Nutrition
Vitamins and Minerals
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Enzymes
Genetics
Genetics
Chromosomes
DNA
Mendel and Heredity
Hereditary Patterns
Proteins and Amino Acids
Plants
Photosynthesis
Plant Structure
Plant Defenses
Flowering Plants
Non-Flowering Plants
Trees
|
Living Organisms
Scientific Classification
Animals
Bacteria
Protists
Fungi
Viruses
Disease
Infectious Disease
Medicine and Pharmaceutical Drugs
Epidemics and Pandemics
Historical Epidemics and Pandemics
Immune System
Cancer
Concussions
Diabetes
Influenza
|