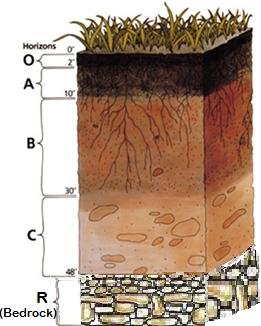
- Organic - The organic layer (also called the humus layer) is a thick layer of plant remains such as leaves and twigs.
- Topsoil - Topsoil is considered the "A" horizon. It is a fairly thin layer (5 to 10 inches thick) composed of organic matter and minerals. This layer is the primary layer where plants and organisms live.
- Subsoil - Subsoil is considered the "B" horizon. This layer is made primarily of clay, iron, and organic matter which accumulated through a process called illuviation.
- Parent material - The parent material layer is considered the "C" horizon. This layer is called the parent material because the upper layers developed from this layer. It is made up mostly of large rocks.
- Bedrock - The bottom layer is several feet below the surface. The bedrock is made up of a large solid mass of rock.
|
|